Pharmacy refers to the health care profession that deals with both the fields of health science as well as chemistry. It is defined as the profession of the art, science and economics of discovery and preparation from natural and synthetic sources, drugs and non-drug materials needed for the prevention, management and treatment of diseases in man and animals.
The word “pharmacy” was coined from the Greek word “pharmakon” meaning “medicine” or “drug“. Therefore, a pharmacist is a “medicine or drug man“. While the classes of professionals legally permitted to prescribe medications are physicians, dentists, veterinary doctors and senior registered nurses, pharmacists are required by law to be experts in the preparation, preservation, distribution, and handling of drugs.
Contents
Disease continues to trail man since the “Fall of Man” and he has continued to seek ways of curing them. Early studies show that man used clay, mud, leaves and supernatural means for alleviating symptoms of various diseases. Women were reported to be earliest gatherers of medicinal plants but the practice was taken up by men in the society. Below were ancient methods used in the treatment of diseases;
This knowledge of medicine was based on observations and experience and not on scientific knowledge. This led to the discoveries of liquorice for cough in Babylonia, rhubarb roots as purgative in China and dried blueberries as anti-diarrhoea in Syria.
The use of incantations, charms, and herbs in “curing” diseases perceived to be spiritual was common in ancient practice of medicine. Also, use of foul smelling urine and dungs were believed to drive away evil spirits.
As man’s curiosity grew, he began to link causative and curative agents and came up with the idea that a symptom of a disease is an indication that a plant or plant part will be effective for its treatment. It was more psychological than scientific. Examples include worm-like roots for treating worm infestation, heart-shaped leaves of Melissa for treating heart diseases, yellow juice of celandine for treating jaundice.
Though the ancient man’s quest for solution to disease was primitive and non-scientific, he had a measure of success motivated by observations, assumptions, and spiritism.
Read Also: How To Become A Pharmacist in 4 Steps
Some notable nations contributed to the development of the medical profession in the early times. Important amongst them are
Pharmacy profession experienced a vast growth in Europe especially with the evolution of new study areas like biochemistry, microbiology, and biology. The 19th century welcomed the discovery of important alkaloids such as morphine, quinine, and emetine. Notable contributors are highlighted below;
These men shaped the atmosphere and further development of the pharmacy profession in Europe while their counterpart in the United States of America with great contributions were Louis Herbert, John Winthrop, Christopher Marshall and William Procter (Father of American Pharmacy).
Read Also: Nations and their contributions to the growth of pharmacy.
The trend of pharmacy practice shows that the practice is becoming more patient-oriented and no longer product-based. The role of the pharmacist has shifted from the classical “lick, stick and pour” dispensary role to being an integrated member of the health care team directly involved in patient care. This challenge has brought about the emergence of clinical pharmacy in the curriculum and the introduction of the Doctor of Pharmacy (Pharm D.) programme to train clinically oriented pharmacists who will aid in providing rational pharmaceutical drug services.
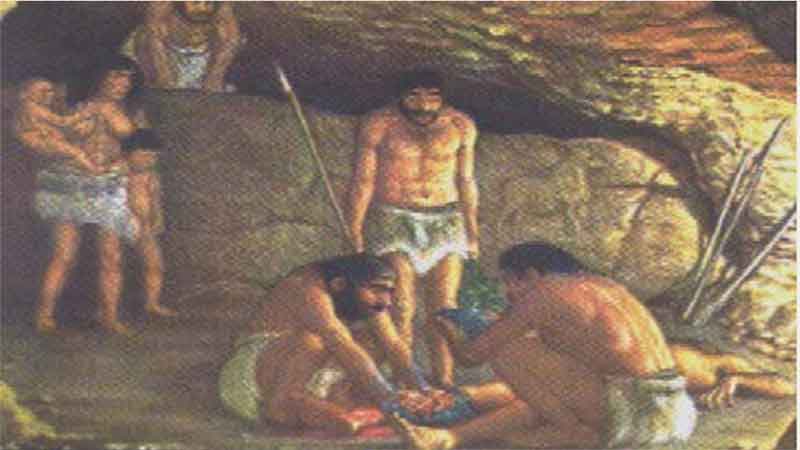 2. Pharmacy in Ancient Babylonia
2. Pharmacy in Ancient Babylonia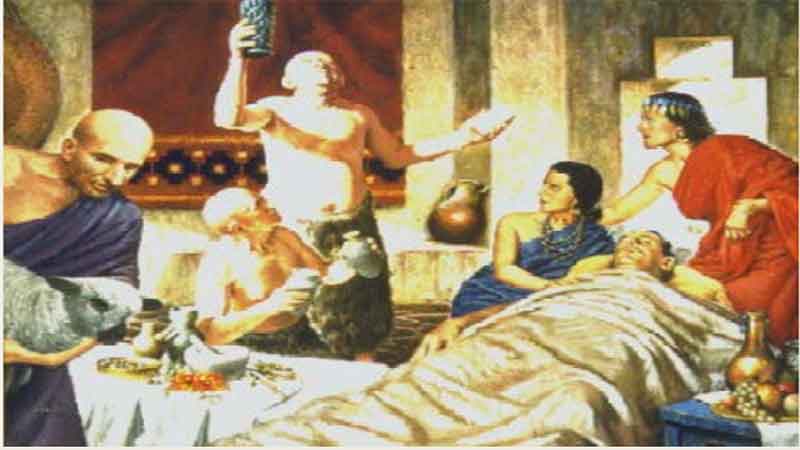 3. Pharmacy in Ancient China
3. Pharmacy in Ancient China 4. Days of the Papyrus Ebers
4. Days of the Papyrus Ebers 5. Theophrastus – Father of Botany
5. Theophrastus – Father of Botany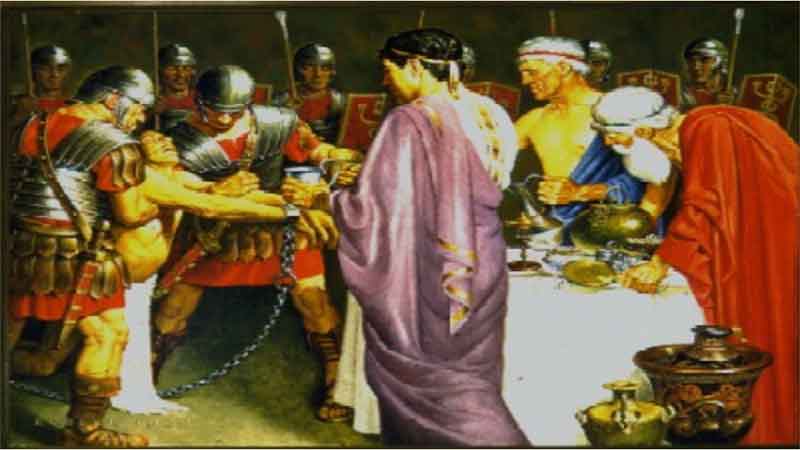 7. Terra Sigillata – An Early “Trademarked
7. Terra Sigillata – An Early “Trademarked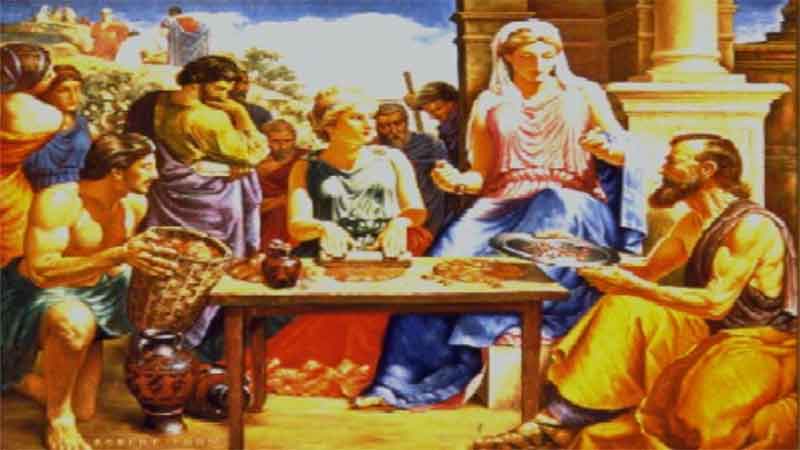
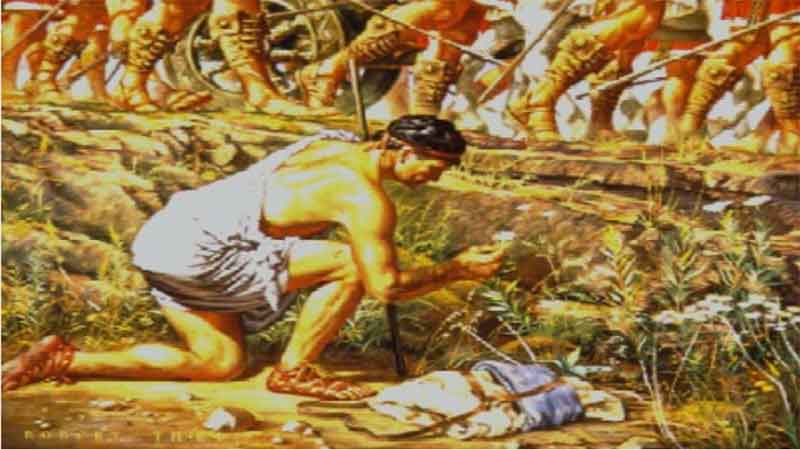 9. Galen – Experimenter in Drug Compounding
9. Galen – Experimenter in Drug Compounding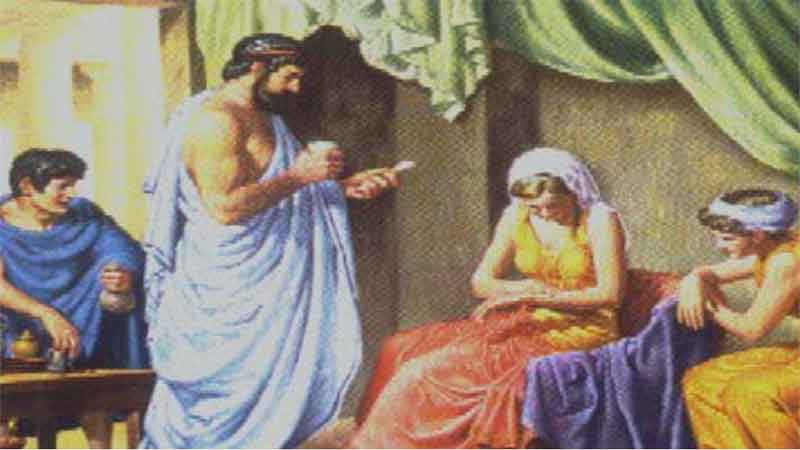 10. Damian and Cosmas – Pharmacy’s Patron Saints
10. Damian and Cosmas – Pharmacy’s Patron Saints 11. Monastic Pharmacy
11. Monastic Pharmacy 12. The First Apothecary Shops
12. The First Apothecary Shops 13. Avicenna – The “Persian Galen”
13. Avicenna – The “Persian Galen” 14. Separation of Pharmacy and Medicine
14. Separation of Pharmacy and Medicine 15. The First Official Pharmacopeia
15. The First Official Pharmacopeia 16. The Society of Apothecaries of London
16. The Society of Apothecaries of London 17. Louis Hébert, Apothecary to New France (Canada)
17. Louis Hébert, Apothecary to New France (Canada) 18. The Governor who Healed the Sick
18. The Governor who Healed the Sick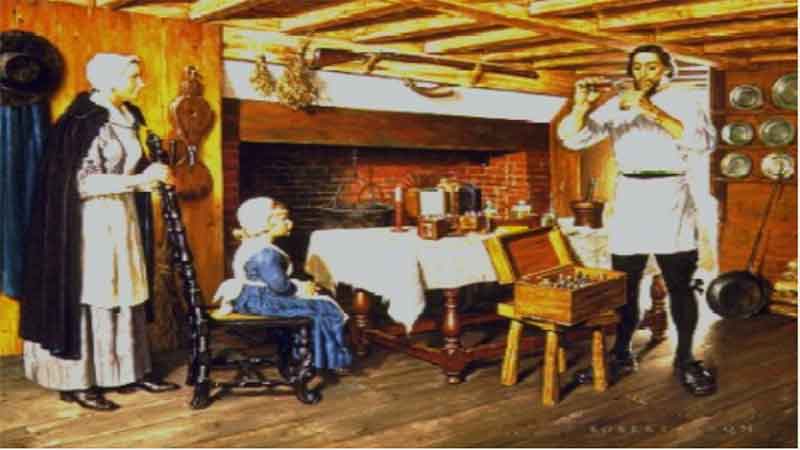 19. The Marshall Apothecary
19. The Marshall Apothecary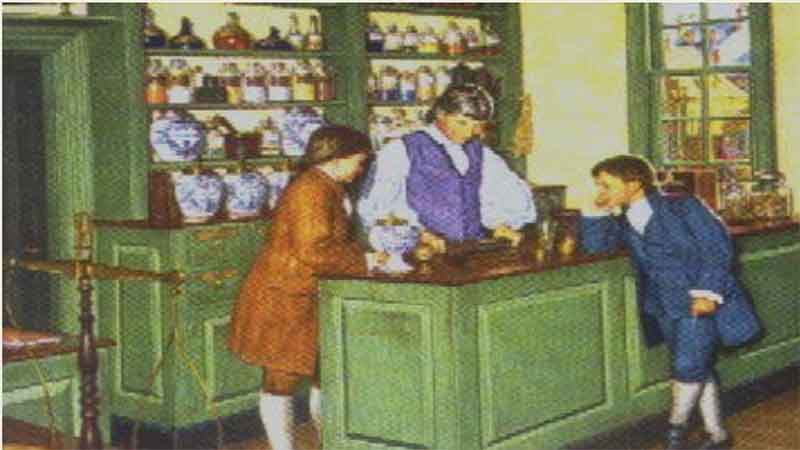 20. First Hospital in Colonial America
20. First Hospital in Colonial America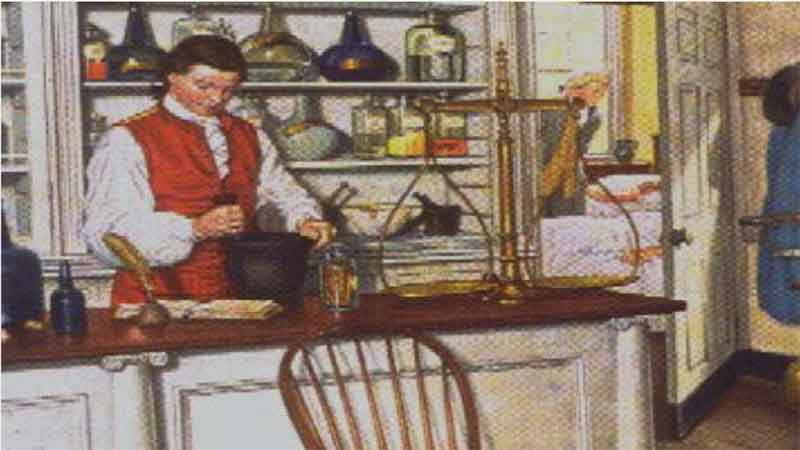 21. Scheele – Greatest of the Pharmacists-Chemists
21. Scheele – Greatest of the Pharmacists-Chemists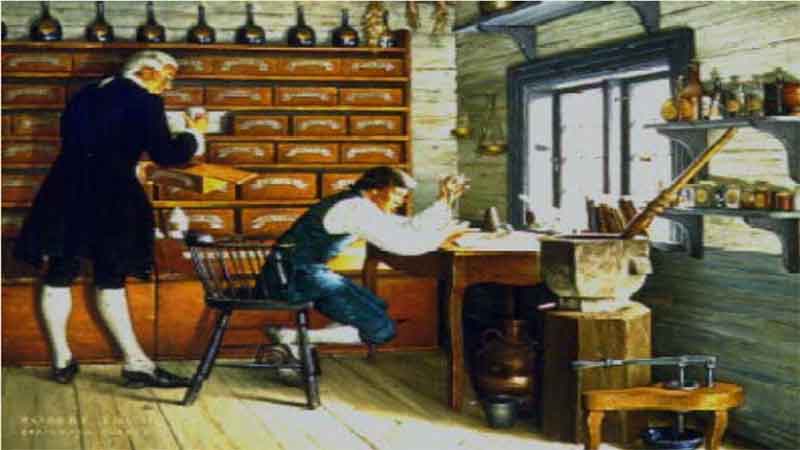 22. Craigie – America’s First Apothecary General
22. Craigie – America’s First Apothecary General 23. Sertürner – First of the Alkaloid Chemists
23. Sertürner – First of the Alkaloid Chemists 24. Caventou, Pelletier and Quinne
24. Caventou, Pelletier and Quinne  25. American Pharmacy Builds its Foundations
25. American Pharmacy Builds its Foundations 26. The Shakers and Medicinal Herbs
26. The Shakers and Medicinal Herbs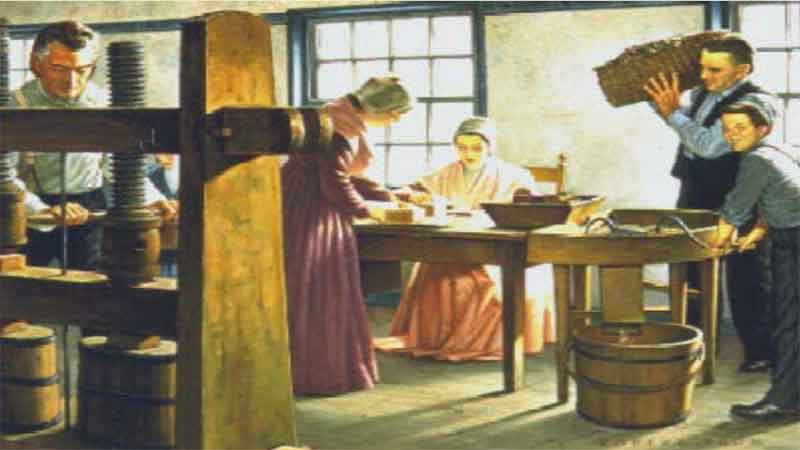 27. The American Pharmaceutical Association
27. The American Pharmaceutical Association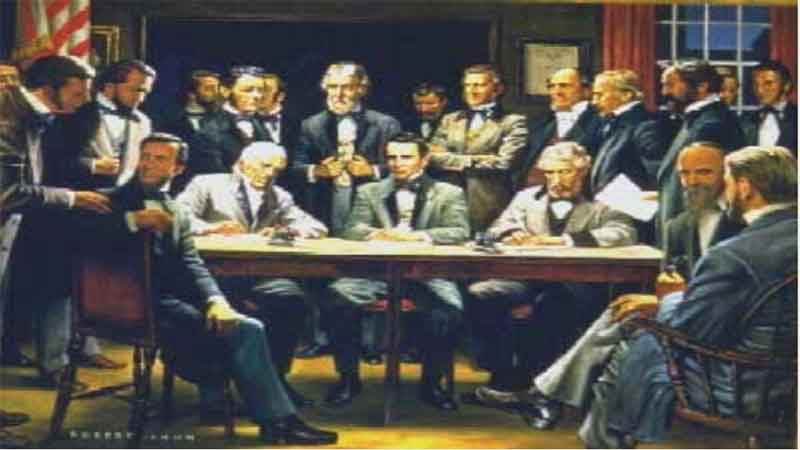 28. European and American Pharmacy Meet
28. European and American Pharmacy Meet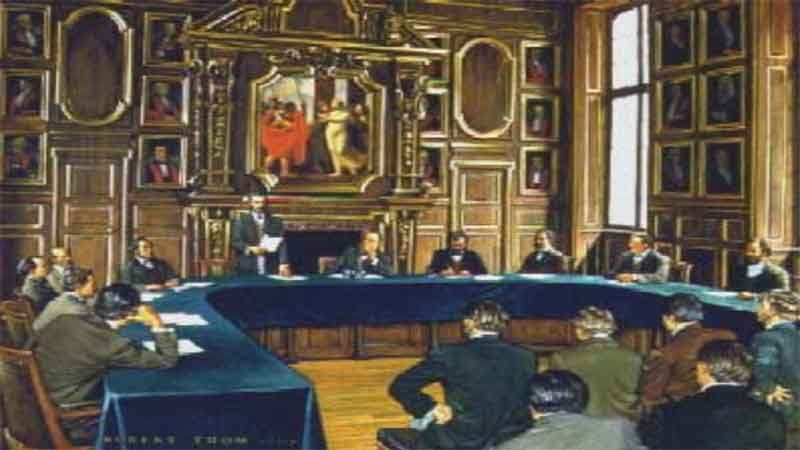 29. The Father of American Pharmacy
29. The Father of American Pharmacy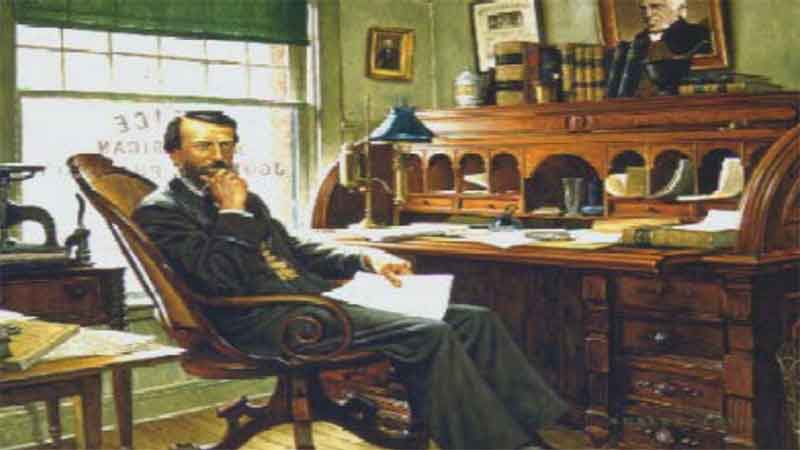 30. A Revolution in Pharmaceutical Education
30. A Revolution in Pharmaceutical Education 31. The Pharmacopeia Comes of Age
31. The Pharmacopeia Comes of Age 32. The Standardization of Pharmaceuticals
32. The Standardization of Pharmaceuticals 33. Wresting the Jungle’s Secrets
33. Wresting the Jungle’s Secrets 34. Stanislas Limousin – Pharmacal Inventor
34. Stanislas Limousin – Pharmacal Inventor 35. The Era of Biologicals
35. The Era of Biologicals 36. The Development of Chemotherapy
36. The Development of Chemotherapy 37. Pharmaceutical Research
37. Pharmaceutical Research 38. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Comes of Age
38. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Comes of Age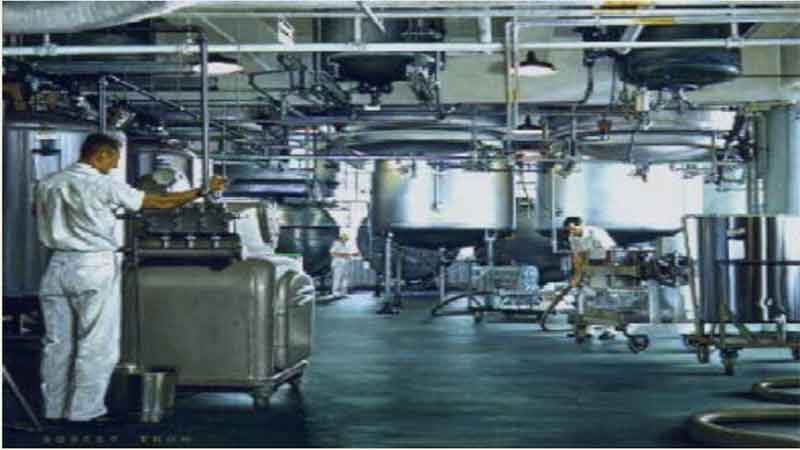 39. The Era of Antibiotics
39. The Era of Antibiotics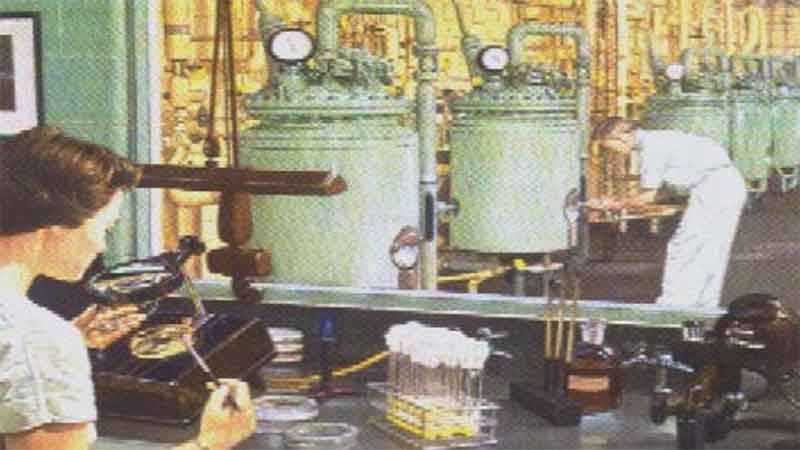 40. Pharmacy Today and Tomorrow
40. Pharmacy Today and Tomorrow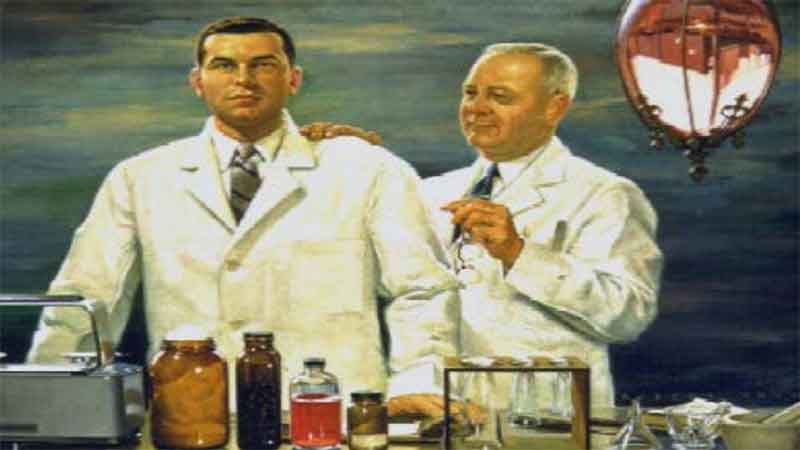
This article “History of Pharmacy” discussed the origin of the word pharmacy, the history of pharmacy with respect to ancient methods used in the treatment of diseases and the history of pharmacy with respect to ancient nations that contributed to its growth. The article “History of Pharmacy” also showed the history of pharmacy in pictures. Keywords: What is History of Pharmacy?, When did Pharmacy begin?, Who is known as father of pharmacy?, Who started pharmacy?, history of pharmacy pdf, history of pharmacy in Nigeria, history of pharmacy profession, history of pharmacy pdf download, important events that contributed to the history of pharmacy, history and evolution of pharmacy, history of pharmacy book, history of pharmacy article.
Comments2
I very excited to know the brief history about my profession,
keep it up it really helped.
I am happy you found helpful.