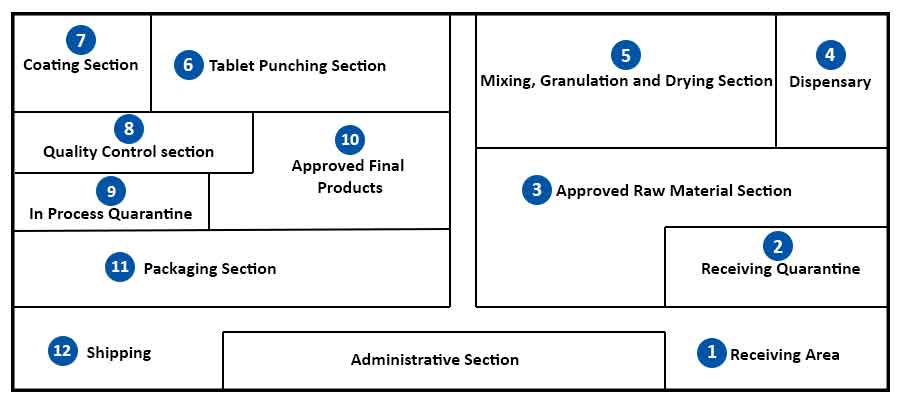
The design and manufacture of pharmaceutical tablets is a complex multi-stage process whereby formulation scientists ensure that the correct amount of drug substance in the right form is delivered at the appropriate time, at the proper rate and in the desired location with its chemical integrity protected to that point. Most drug substances do not possess the required properties which give satisfactory flow from the hopper to the die cavity of tablet presses. As a result, they are subjected to pre-treatment either alone or in combination with suitable excipients to form free-flowing granules that lend themselves to tabletting.
Tablets are commonly manufactured by wet granulation, dry granulation or direct compression. These methods may be considered to consist of a series of steps (unit processes) – weighing, milling, mixing, granulation, drying, compaction, (frequently) coating and packaging. Regardless of the method used the unit processes – weighing, milling and mixing, are the same; subsequent steps differ.
Contents
The primary goals include:
In general, the choice of formulation process employed during tablet manufacture is dependent upon such factors as:
In addition to the job-specific responsibilities of these personnel, all manufacturing employees must be versed and trained in Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMPs) and in the appropriate Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) governing their area.
Tablets in addition to the therapeutic agent(s) also contain excipients that are required to ensure satisfactory production process. These materials which are inert may be added to the drug substance to increase its bulk and give those desirable properties lacking in the drug substance alone. Depending on the intended use, tablet excipients may be subcategorized into:
Many excipients used in tablet formulation are multi-functional that is, they may serve more than one function and thus can affect the properties of powders or tablets in various ways at varying concentrations.
All excipients used in tablet formulation may not be present in all tablet formula. Some such as lactose, stearates, microcrystalline cellulose are common to the vast majority of tablets. Excipients used in tablet formulations include binders or granulating fluid, diluents, disintegrants, lubricants, glidants, colourants, sweeteners, flavourants, adsorbents, and surfactants.
Read Also: Excipients used in tablet formulation.
Quality control of tablet raw materials (APIs and excipients) is one of the main tasks of the quality control unit in any drug manufacturing industry. Raw materials described in monograph of relevant Pharmacopoeia must undergo the necessary tests as stated in the monograph. It is often sufficient if identification testing is conducted on the individual packages/containers and content and purity determination in mixed samples.
Every manufacturer has the opportunity to carry out further testing if they deem it necessary for guaranteeing a smooth-running production process or a very high-quality product. Starting materials are released only after their quality are established or judged as satisfactory. Raw materials that fail the quality control test are rejected and returned to the supplier.
Any risks that may emanate from starting materials of inappropriate quality must be avoided to prevent product failure and to ensure a consistent level of quality, as well as safety in consumer and industrial products.
Common equipment used in pharmaceutical tablet manufacturing include:
Tablet Manufacturing Equipment continues to improve in both production speed and uniformity of the tablets compressed.
Some of the steps above are skipped depending on the manufacturing process used during tablet formulation.
Tablets are commonly manufactured by
One important requirement is that the drug mixture flows freely from the hopper of the tabletting machine into the dies to enable high-speed compression of the powder mix into tablets.
Wet granulation is a widely used method for the production of compressed tablet. It is essentially a process of size enlargement involving several steps and the use of an adhesive substance known as binder. The granules produced using this method of granulation has a greater probability of meeting all the physical requirements for tablet formation.
A stepwise summary of the manufacturing steps used in the manufacture of tablets by the wet granulation method are listed below.
Tablets manufactured by wet granulation exhibit sufficient mechanical properties to be subsequently exposed to other unit operations, e.g. film coating.
Read: Manufacture of tablets by wet granulation method
The formation of granules by compacting powder mixtures into large pieces or compacts which are subsequently broken down or sized into granules (often referred to as dry granulation, double compression or pre-compression) is a possible granulation method which, however, is not widely used in the manufacture of tablets. This method is used when tablet excipients have sufficient inherent binding properties. The procedure can also be used as a means to avoid exposure of drug substances to elevated temperatures (during drying) or moisture. Double compression method eliminates a number of steps but still includes weighing, mixing, slugging, dry screening, lubrication, and compression of granules into tablets. Compaction for the dry granulation process is generally achieved either by slugging or roller compaction.
In this method, the powder mix is compressed into a soft large flat tablet (about 1 inch in diameter) using a tablet press that is capable of applying high stress. Following this, the slugs are broken by hand or milled using conventional milling equipment to produce granules of the required size. Lubricant is added in the usual manner, and the granules then compressed into tablets. Aspirin is a good example of where slugging is satisfactory. Other materials, such as aspirin combinations, acetaminophen, thiamine hydrochloride, ascorbic acid, magnesium hydroxide, and other antacid compounds, may be treated similarly.
Results similar to those accomplished by the slugging process are also obtained with powder compactors. In roller compaction method, the formulation ingredients are mixed and are passed between high-pressure (oppositely) rotating rollers that compress the powder at 1 to 6 tons of pressure. The compacted material is then milled to a uniform granule size and compressed into tablets after the addition of a lubricant. The roller compaction method is often preferred to slugging. Excessive pressures that may be required to obtain cohesion of certain materials may result in a prolonged dissolution rate.
Read: Manufacture of tablets by dry granulation method
A stepwise summary of the manufacturing steps used in the manufacture of tablets by the dry granulation method are listed below.
As its name implies, direct compression involves direct compression of powdered materials into tablets without modifying the physical nature of the materials itself. The technology involved in this method assumes great importance in the tablet formulations, because it is often the cheapest means, particularly in the production of generics that the active substance permits. Direct compression avoids many of the problems associated with wet and dry granulations. Its successful application in tablet formulation rests on two fundamental issues:
A stepwise summary of the manufacturing steps used in the manufacture of tablets by the dry granulation method are listed below.
It is worth noting that tablets produced by direct compression are often softer than their counterparts that have been produced by wet granulation and therefore they may be difficult to film-coat.
Read: Manufacture of tablets by direct compression method
Read Also: Common Defects in Film Coating Process: Causes and Possible Solutions
Tablets should be subjected to a number of tests before they are deemed fit for marketing and consumption. These tests can be divided into two broad categories namely
Read Also: Quality Control Tests for Tablets
Before tablets are sent out for distribution, they are usually packaged using appropriate packaging materials. The type of packaging material used is a matter of choice and is dependent on several factors including:
Tablets are commonly packaged using blister and strip packs and are kept in places of low humidity, and protected from extremes temperature. The packaging provides excellent environmental protection for each unit of tablet, coupled with an aesthetically pleasing and efficacious appearance. Blister and strip packaging also provide some degree of tamper resistance to the dosage form.
For larger quantities delivered to the pharmacist, glass or plastic bottles, metal containers, cartons, or paperboard drums may be used along with polyethylene liners, where necessary, to give added protection from moisture. If cotton wool stuffing is used under these circumstances it is an advantage for it to be external to the liners so that any moisture that it contains does not gain access to the tablets. Tablets that are decomposed when exposed to moisture can also be packaged with a desiccant packet. Light sensitive tablets are packaged in light-resistant containers. With a few exceptions, tablets that are properly stored will remain stable for many years.
Reference
The title of this article is Manufacture of Pharmaceutical Tablets. This article;Manufacture of Pharmaceutical Tablets gives an overview of tablet formulation processes..Related keywords: Manufacture of Pharmaceutical Tablets, tablet manufacturing process slideshare, basics of tablet manufacturing, tablet manufacturing process pdf, manufacturing of tablets and capsules, tablet manufacturing equipment pdf, tablet formulation, tablet capsule manufacturing process, pharmaceutical tablet size chart.
Comments12
Thank You for your continued commitment to the profession.
Cordially,
Vincent
very nice article . Thanks for sharing .
You are welcome. I am glad you found it useful.
it is useful to me . i already have 26 years experience in production of pesticides and plant growth regulator ,q,c by glc ,hplc , supervision and packing. to meet the India s covid 19 current requirement of hydroxy chloroquine tablets i want additional knowledge about tablet manufacturing .
thanks for your wide in formation .
Thank you soo much. As a pharmacy Student, this helped me soo much with my Pharmaceutical Technology modules.
Continue help us through your writings.
I am happy you found it useful.
Presented very nicely. Thank you for the excellent presentation.
You are welcome.
Mashallh
This article was so fine and useful alhmdllhi. May God reward you sir. I found it very very useful.
Thanks.
You guys have very informatie articles. I am reading these articles for my PSU
pharmacy eligibility exam, but iam learning a lot. Thank you very much Pharmapproach
You are welcome.